Comparative Analysis of Asynchronous Machines and Synchronous Counterparts
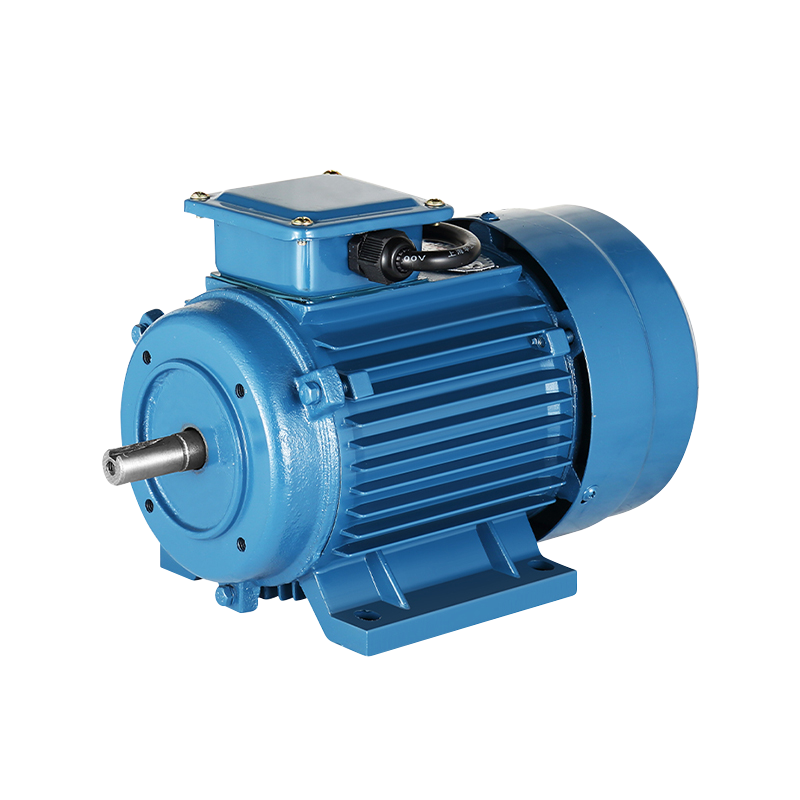
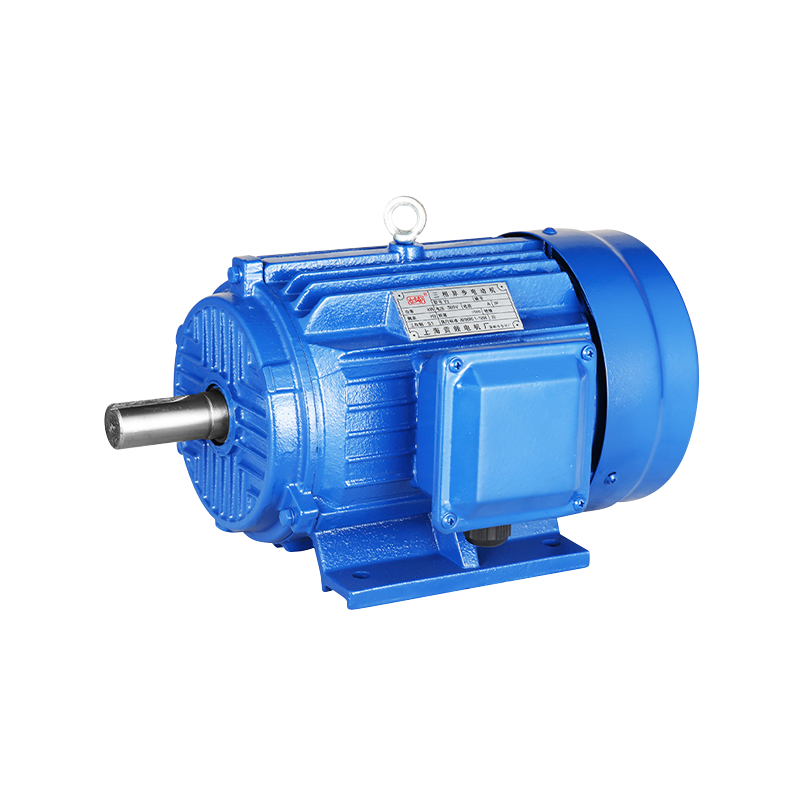
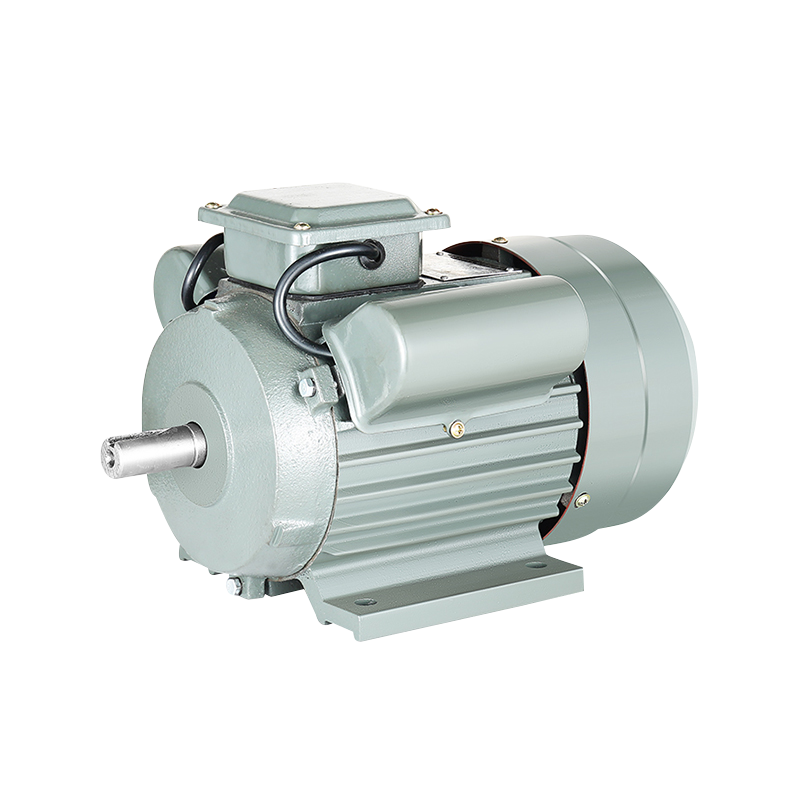
China Wholesale Asynchronous Three Phase Traction Motor Machine Factory
In the realm of electrical engineering, the choice between Asynchronous Machines and Synchronous Machines often hinges on specific application requirements. Both types of machines are integral to the generation, transmission, and distribution of electrical power. This article aims to provide a comparative analysis of China Asynchronous Machines and their synchronous counterparts, examining their operational principles, efficiency, and suitability for various applications.
Asynchronous Machines, also known as induction machines, derive their name from the fact that the speed of the rotating magnetic field within the machine is not synchronized with the speed of the rotor. This difference in speed, known as slip, is what allows it to transfer power from the stator to the rotor. The simplicity of it, with no brushes or slip rings, makes it a popular choice for many industrial applications.
When comparing the efficiency of Asynchronous Machines to their synchronous counterparts, it's important to consider the specific context. Synchronous Machines are often more efficient at higher power levels and constant speed applications, such as in large power plants. However, it can be more efficient in variable speed applications and smaller power ranges, such as in local grid systems or industrial drives.
The suitability of Asynchronous Machines in renewable energy systems is a topic of significant interest. They are particularly well-suited for wind power generation due to their ability to operate over a wide range of speeds, which is beneficial for variable wind conditions. In contrast, Synchronous Machines require a constant speed to maintain a stable output, making them less flexible in this regard.
One of the key advantages of Asynchronous Machines is their reliability and low maintenance requirements. The absence of brushes and slip rings reduces the need for regular maintenance, which is a significant advantage in remote or hard-to-reach locations, such as offshore wind farms. Synchronous Machines, on the other hand, may require more frequent maintenance due to their more complex construction.
The control and speed regulation of Wholesale Asynchronous Three Phase Motors are relatively straightforward compared to Synchronous Machines. The induction motor can be easily controlled by a frequency converter (variable frequency driver), which adjusts the power frequency to change the motor speed. Synchronous Machines, however, require more complex control systems to maintain a constant speed, which can add to the overall cost and complexity of the system.
When considering the integration of Asynchronous Machines with grid systems, their ability to provide reactive power support is a notable advantage. It can operate in a manner that helps maintain the power factor of the system, which is crucial for stable grid operation. Synchronous Machines also provide reactive power support, but their control is more complex and typically requires additional equipment.
The environmental impact of Asynchronous Machines is generally lower due to their simpler design and fewer moving parts. This results in less material usage and lower waste generation at the end of their service life. Synchronous Machines, with their more complex construction, can have a higher environmental footprint, although this can be mitigated through careful design and material selection.
In terms of cost, Asynchronous Machines often have a lower initial investment cost due to their simpler design. However, the total cost of ownership must also consider maintenance, efficiency, and lifespan. Synchronous Machines may have a higher initial cost but can offer better efficiency and longer service life in certain applications, which can offset the initial investment over time.
The comparative analysis of Asynchronous Machines and Synchronous Machines reveals that each has its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Asynchronous Traction Motor Factory excels in applications requiring variable speed operation, low maintenance, and simple control systems. They are particularly well-suited for integration with renewable energy systems, where their ability to handle variable speeds and provide reactive power support is invaluable. Synchronous Machines, while more complex and requiring higher initial investment, offer efficiency and constant speed operation, which is beneficial in large-scale power generation and grid stability. The choice between Asynchronous Machines and Synchronous Machines will continue to depend on the specific requirements of each application, and as technology advances, we can expect both types of machines to evolve to meet the challenges of a more sustainable and efficient energy future.
-
Feedback

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体