Author: Admin Date: 2023-12-28
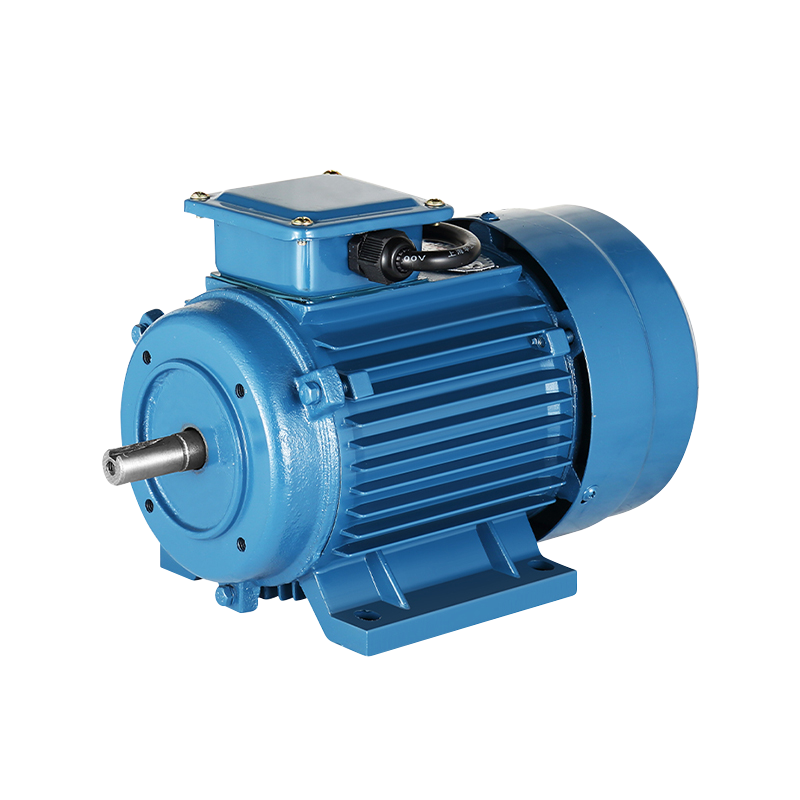
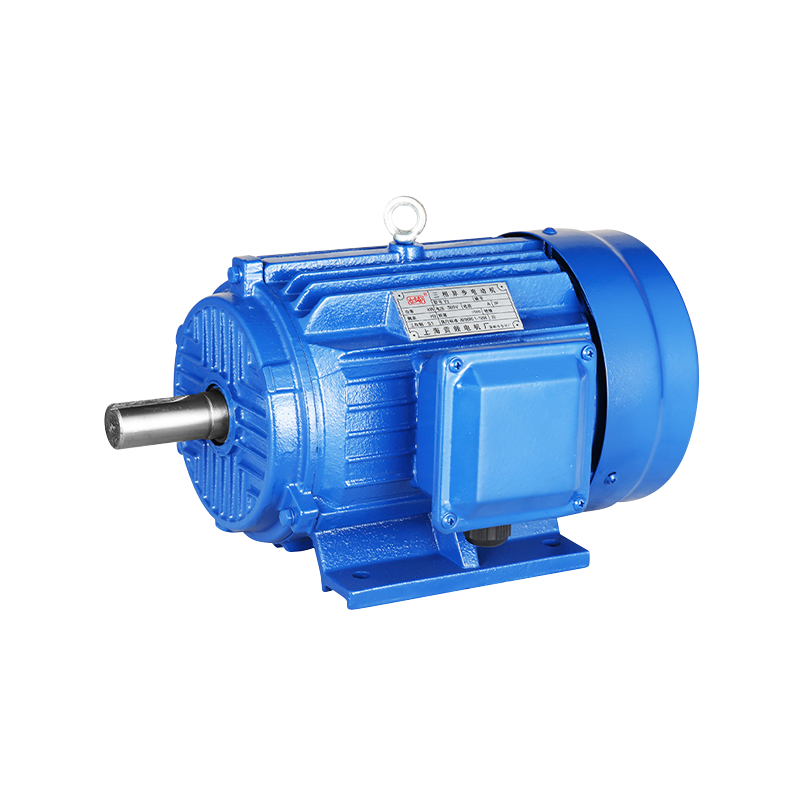
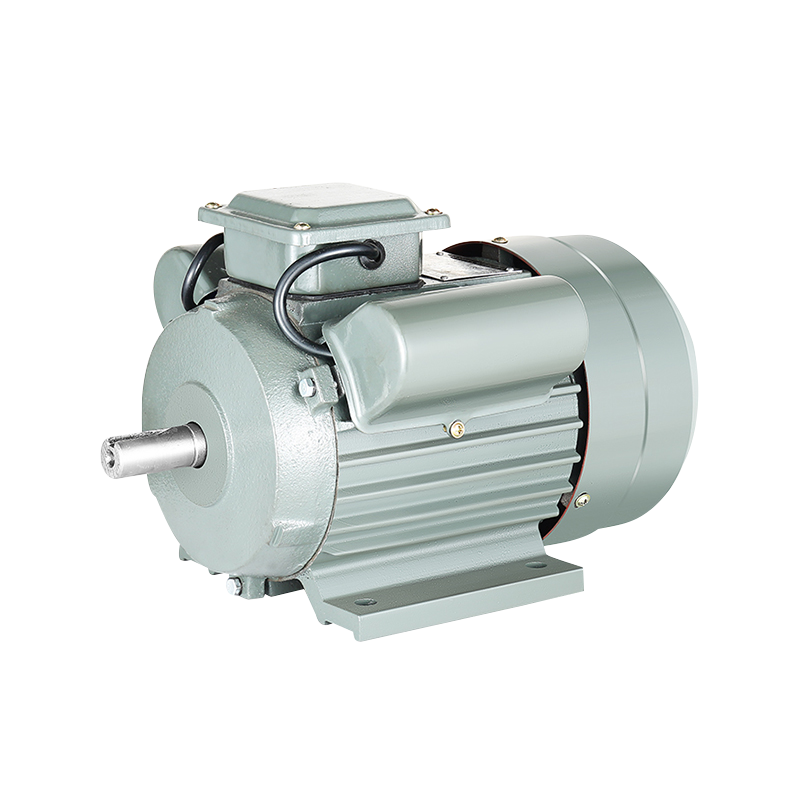
What is an asynchronous motor
An asynchronous motor, also known as an induction motor, is an AC motor that generates electromagnetic torque by interacting with the air gap rotating magnetic field and the induced current of the rotor winding, thereby converting electromechanical energy into mechanical energy.
Asynchronous motors are divided into two forms according to the rotor structure: squirrel cage type (squirrel cage asynchronous motor) and wound type asynchronous motor.
Asynchronous motor for motor operation. Because the rotor winding current is generated by induction, it is also called an induction motor. Asynchronous motors are widely used and in demand among all types of motors. About 90% of the electricity-powered machinery in various countries are asynchronous motors, of which small asynchronous motors account for more than 70%. In the total load of the power system, the electricity consumption of asynchronous motors accounts for a considerable proportion. In China, the electricity consumption of asynchronous motors accounts for more than 60% of the total load.
An asynchronous motor is an AC motor, and the ratio between its speed under load and the frequency of the connected grid is not a constant value. An induction motor is asynchronous with only one set of windings connected to the power supply. Without causing misunderstanding and confusion, induction motors can generally be called asynchronous motors. The IEC standard states: The term "induction motor" is used as a synonym for "asynchronous motor" in many countries, while some other countries only use the term "asynchronous motor" to represent these two concepts.
-
Feedback

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体